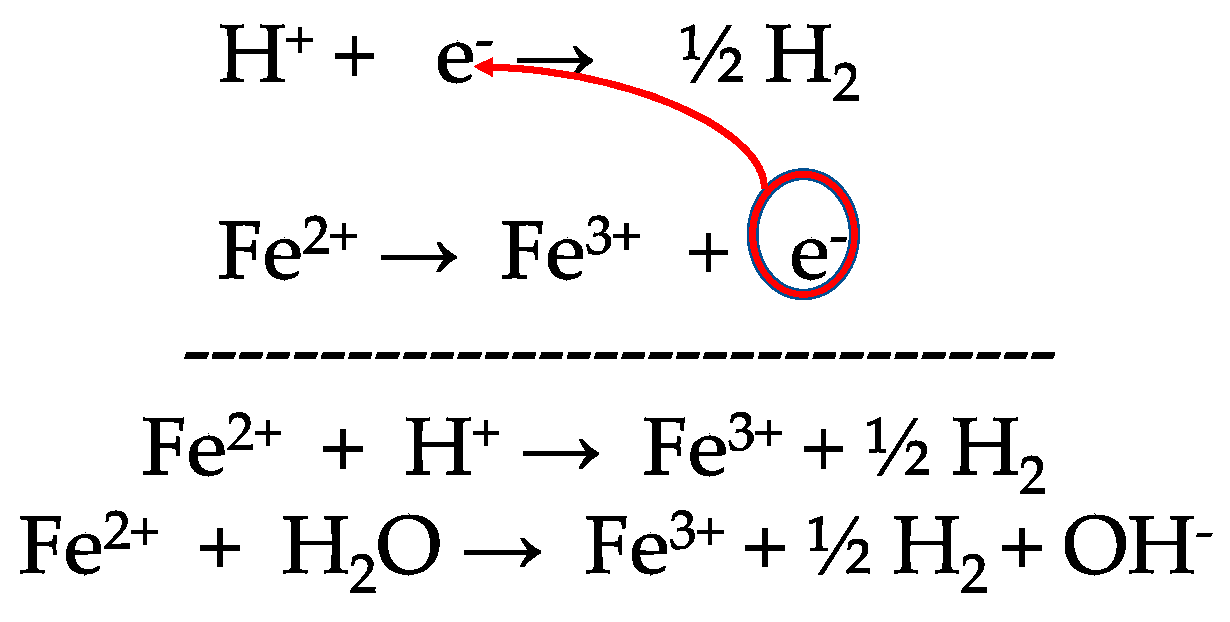Given standard electrode potentials, Fe^2 + 2e^-→ Fe, E^∘ = - 0.440 V Fe^3 + + 3e^-→ Fe, E^∘ = - 0.036 V The standard electrode potential (E^∘) for Fe^3 + + e^-→ Fe^2 + is:

Homogeneous photocatalytic Fe3+/Fe2+ redox cycle for simultaneous Cr(VI) reduction and organic pollutant oxidation: Roles of hydroxyl radical and degradation intermediates - ScienceDirect

Schematic of intestinal iron uptake. Fe3+ in the intestinal lumen is... | Download Scientific Diagram

SOLVED: Description Draw the potential - pH diagram for Fe2+ Fe3+ Fe(OHJz, Fe(OH)g. Take the concentration of Fe2+and Fe3+as IM in all equations. Fe2++ 2e –> Fe NHE EO= -0.44 V vs

SOLVED: QUESTion points Save Anawor If a Galvanic cell is created using the Ag+/Ag and Fe2+/Fe3t half reactions, what is the net reaction for this electrochemical cell? Fe3-(aq) Ag"(aq) Fe?+(aq) Agls) Fe?-(aq)

Fe2+/Fe3+ Cycling for Coupling Self‐Powered Hydrogen Evolution and Preparation of Electrode Catalysts - Chen - 2022 - Angewandte Chemie International Edition - Wiley Online Library

Double-enzymes-mediated Fe2+/Fe3+ conversion as magnetic relaxation switch for pesticide residues sensing - ScienceDirect

Inhibition of Fe2+- and Fe3+- induced hydroxyl radical production by the iron-chelating drug deferiprone - ScienceDirect

Roles of Fe2+, Fe3+, and Cr3+ surface sites in the oxidation of NO on the (Fe,Cr)3O4(1 1 1) surface termination of an α-(Fe,Cr)2O3(0 0 0 1) mixed oxide - ScienceDirect


.PNG)